




This tool allows you to deform a model globally or locally. You specify the deformation by deforming a bounding box that surrounds the object.
|
|
There are:
Local deformers:
Local deformers use the NURBS methods to mold polygonal objects. As with NURBS models, you will act on the control points of a bounding box, not on the points of the surface of the object. You will get local deformations and the object will remain smooth like a NURBS object.
Global deformers:
Global deformers allow you to deform the whole object. You will act on the bounding box and not on control points.
![]()
This tool does not use Dynamic Geometry properties. In fact, it will delete the D.G. properties (if any) of your object, and you will no longer be able to use the features of D.G. to modify your object. (Amapi 3D will not display the palette described above for this object).
If you want your object to retain its D.G. properties, do not use any of these tools on it.
See chapter User Manual/The objects/Dynamic Geometry.
q The local deformers: Stretch, Scale, Rotate
Usage:
1. Selecting a polygonal object.
Using the Wand, click on a polygonal object or group of objects to designate the current object.
To restrict the action to a part of the element, use the Lasso or the Bullseye through the Assistant Palette or using the hotkey (PC: Click on the right mouse button, Mac: Option-click).
2. Selecting the Deformation tool.
Click on the icon depicting the tool in the Tools Palette.
A meshed control box encloses the object.
The default density of the mesh is 3x3x3. This is the minimum density.
3. Defining the control box’s mesh density.
You can do this in several ways:
· Use the “+” and “-” keys of the numeric keypad. Amapi 3D will increase or decrease the number of control polygons on all three axes.
· Use the “+” or “–” buttons of the Assistant Palette. Amapi 3D will increase or decrease the number of control polygons on all three axes.
· Press the Tab key, enter the number of control polygons per axis, then press the Return key to validate.
4. Editing the control box.
The deformation box is now the current object. You will model the object through it: the model will be distorted per the distortions applied to the control box. Amapi 3D provides three tools for your use:
· Stretch
· Scale
· Rotate
See the chapter User Manual Tools/Modeling/Stretch, Scale, Rotate for a detailed description of each of these tools.
5. Ending the tool action.
Put the tool aside to end the action (depending on the interface). See chapter User Manual/Tools/Generic use of a tool/How do you end a tool action?
|
Practical exercises:
|
Original object |
Tapered object |
Twisted object |
Bent object |
|
|
|
|
Original object |
Tapered object |
Expanded object |
Usage:
1. Selecting an object.
Select the object to be deformed.
You can restrict the action to a part of the object by using the Lasso or the Bullseye. (See chapter User manual/ Modeling help tools / Assistant Palette / Selection accessories).
2. Selecting the Deformer tool.
Click on the icon depicting the Deformer tool. A meshed control box encloses the object.
The default is the Stretch tool.
3. Selecting the Taper tool.
Click on the icon depicting the Taper tool. A yellow control box encloses the object.
4. Select the axis of the action.
Press the spacebar to toggle the axis of deformation: width or height.
5. Specify the face that will control the action.
Click on the face that you will use to control the deformation.
6. Taper or expand the object.
The data palette displays the ratio between the expected size of the control face and the initial size.
Set this value and go to the next step, or go back to steps 4 or 5.
There are several ways to modify this data:
With the mouse:
Move the cursor to increase or decrease the size of the control face. The whole object is deformed interactively, depending on your action on the control face.
When the deformation is the way you want, click to validate.
“Remote” interaction:
You can modify the ratio value in “remote” mode, as follows:
- Use the Tuner “+” and “-” keys or the “+” and “-” icons of the Assistant Palette.
- Use the Remote Control (see User Manual/Tools/The data window/Distant interaction/The remote control).
- Use the Slider (see User Manual/Tools/The data window/Distant interaction/The slider).
Numerical data:
If you prefer to specify the value numerically,
Press the Tab key.
Enter a numerical value.
Validate.
7. Ending the tool action.
End the tool action by putting the tool aside (depending on the interface). (see User Manual/Tools palette/General tool usage/How to end an action).
|
Practical exercises:
|

This tool allows you to act on a face of the bounding box to twist it around its center of gravity (about its vertical or horizontal axis).
The object will follow the deformation.
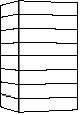
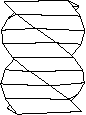
Original object Twisted object
Usage:
1. Selecting an object.
Select the object to be deformed.
You can restrict the action to a part of the object by using the Lasso or the Bullseye. (See chapter User manual/ Modeling help tools / Assistant Palette / Selection accessories).
2. Selecting the Deformer tool.
Click on the icon depicting the Deformer tool. A meshed control box encloses the object.
The default is the Stretch tool.
3. Selecting the Twist tool
Click on the icon depicting the Twist tool. A yellow control box encloses the object.
4. Select the axis of the action.
Press the spacebar to toggle the axis of deformation: width or height.
5. Specify the face that will control the action.
Click on the face that you will use to control the deformation.
6. Twist the object.
The data palette displays the angle of rotation about which the control face will rotate around its center of gravity.
Set this value and go to the next step, or go back to steps 4 or 5.
There are several ways to modify this data:
With the mouse:
Move the cursor to move the control face. The whole object is deformed interactively, depending on your action on the control face.
When the deformation is the way you want, click to validate.
“Remote” interaction:
You can modify the ratio value in “remote” mode, in one of the following ways:
- Using the Tuner “+” and “-” keys or the “+” and “-” icons of the Assistant Palette.
- Using the Remote Control (see User Manual/Tools/The data window/Distant interaction/The remote control).
- Using the Slider (see User Manual/Tools/The data window/Distant interaction/The slider).
Numerical data:
If you prefer to specify the value numerically,
Press the Tab key.
Enter a numerical value.
Validate.
7. Ending the tool action.
End the tool action by putting the tool aside (depending on the interface). (see User Manual/Tools palette/General tool usage/How to end an action).
|
Practical exercises:
|

This tool allows you to act on a face of the bounding box to bend it around its center of gravity (around a horizontal or vertical axis).
The object will follow the deformation

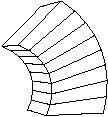
Original object Bent object
Using:
1. Selecting an object.
Select the object to be deformed.
You can restrict the action to a part of the object by using the Lasso or the Bullseye. (See chapter User manual/ Modeling help tools / Assistant Palette / Selection accessories).
2. Selecting the Deformer tool.
Click on the icon depicting the Deformer tool. A meshed control box encloses the object.
The default is the Stretch tool.
3. Selecting the Bender tool.
Click on the icon depicting the Bender tool. A yellow control box encloses the object.
4. Select the axis of the action.
Press the spacebar to toggle the axis of deformation: width or height.
5. Specify the face that will control the action.
Click on the face that you will use to control the deformation.
6. Bend the object.
The data palette displays the angle of rotation with which the control face will rotate around its center of gravity.
Set this value and go to the next step, or come back to steps 4 or 5.
There are several ways to modify this data:
With the mouse:
Move the cursor to move the control face. The whole object is deformed interactively, depending on your action on the control face.
When the deformation is the way you want, click to validate.
“Remote” interaction:
You can modify the ratio value in “remote” mode, in one of the following ways:
· Using the Tuner “+” and “-” keys or the “+” and “-” icons of the Assistant Palette
· Using the Remote Control (see User Manual/Tools/The data window/Distant interaction/The remote control)
· Using the Slider (see User Manual/Tools/The data window/Distant interaction/The slider)
Numerical data:
If you prefer to specify the value numerically,
Press the Tab key.
Enter a numerical value.
Validate.
7. Ending the tool action.
End the tool action by putting the tool aside (depending on the interface). (see User Manual/Tools palette/General tool usage/How to end an action).
|
Practical exercises:
|
